The full name of EMC testing (electromagnetic compatibility testing) is Electro Magnetic Compatibility, which is defined as "the ability of equipment and systems to work normally in their electromagnetic environment and not to cause unbearable electromagnetic disturbance to anything in the environment." This definition contains two This means that, firstly, the equipment should be able to work normally in a certain electromagnetic environment, that is, the equipment should have a certain degree of electromagnetic immunity (EMS); secondly, the electromagnetic disturbance generated by the equipment itself must not cause other electronic products. The big influence is electromagnetic disturbance (EMI).
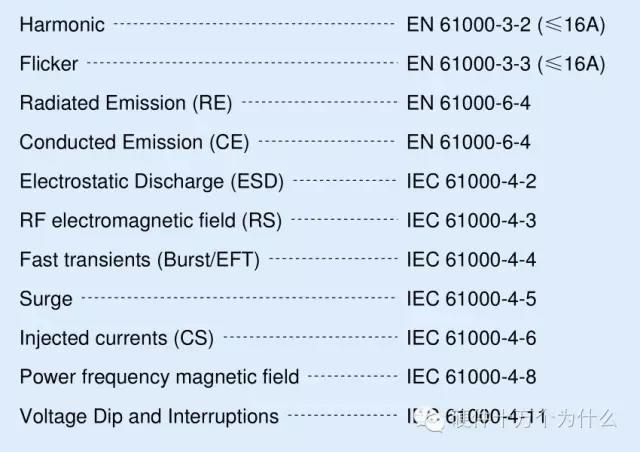
EMI inspection items
①Harmonic current (2~40th harmonic)
②Flash Flicker
③Conducted disturbance (CE)
④Radiation disturbance (RE)
EMS inspection items
①. Electrostatic discharge immunity (ESD);
②. Radiated electromagnetic field (80MHz~1000 MHz) immunity (RS);
③. Electrical fast transient/pulse group immunity; (EFT)
④. Surge (lightning strike) immunity; (Surge)
⑤. Injection current (150kHz~230MHz) immunity (CS);
⑥. Voltage sag and short-term interruption immunity
1. Harmonic (harmonic test)
Standard: EN61000-3-2
a) Specify the limits of harmonic currents emitted to the public grid.
b) Specify the limits of the harmonic components of the input current generated by the device under test in a specific environment.
c) Suitable for electrical and electronic equipment connected to public low-voltage networks with input current less than or equal to 16A.
Harmonic testing is mainly to check the influence of harmonics in the low-voltage power supply network on these frequency-sensitive equipment.
Harmonic experiment principle: Due to the working mode of electronic equipment, non-linear components and various interference noises, the input current is not completely positive glare, and it is often rich in high-order harmonic components that cause pollution to the power grid.
Harmonics in power systems refer to sinusoidal voltages or sinusoidal currents whose frequencies are integer multiples of the rated frequency of the power supply system.
The occurrence of harmonic currents in public transmission systems will cause the following problems:
1. Lose more electric energy, each harmonic has a reactive power part and an active power part, (the active power will heat the wire and cause the wire to use a larger area);
2. The service life of electronic components is shortened;
3. Voltage distortion leads to reduced motor efficiency
2. Voltage fluctuation and flicker Flicker
Standard: EN 61000-3-3
a) Limits on the influence of constant voltage fluctuation and flicker on the public grid.
b) Specify the guidance of the voltage change limit and evaluation method generated by the tested prototype under specific conditions.
c) Applicable to 220V to 250V, 50Hz electrical and electronic equipment connected to the public low-voltage network with an input current of less than or equal to 16A per phase. The purpose of this standard is to ensure that the product does not cause excessive flicker effects on the lighting equipment connected to it (The lights flash).
3. Conducted disturbance CE (0.15-30MHz)
Standard: EN61000-6-4
A) Electrical and electronic measurement and test equipment
B) Electronic and electrical control equipment
C) Electronic and electrical laboratory equipment
Classification of equipment
Class A: (Non-domestic)equipment suitable for use in all establishments other than domestic and those directly connected to a low voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes.
Class B: (Home)equipment suitable for use in domestic establishments and in establishments directly connected to a low voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes.
Principle of Conduction Harassment Experiment:
When the frequency of the interference noise of the electronic equipment is less than 30MHz, it mainly interferes with the audio frequency band. The cable of the electronic equipment is less than one wave of the wavelength of this type of electromagnetic wave (the wavelength of 30MHz is 10m), and the efficiency of radiation into the air is very low. In this way, if the noise voltage induced on the cable can be measured, the degree of electromagnetic noise interference in this frequency band can be measured, and this type of noise is conducted noise.
The role of LISN:
1. High-frequency isolation between the EUT and the power supply is used to prevent noise from the power supply from entering the EUT and affecting the measurement results.
2. Simulate the actual power supply impedance and provide the specified impedance between the power supply terminals of the EUT to unify the measurement results.
3. Maintain a stable impedance of 50 ohms in the test frequency band to match the input impedance of the measurement receiver/spectrum analyzer.
4. Radiation disturbance RE (30-1000MHz)
Standard: EN61000-6-4
a) Electrical and electronic measurement and test equipment
b) Electronic and electrical control equipment
c) Electronic and electrical laboratory equipment
Classification of equipment
Class A: equipment suitable for use in all establishments other than domestic and those directly connected to a low voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes.非家用
Class B: equipment suitable for use in domestic establishments and in establishments directly connected to a low voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for domestic purposes. 家用
Principle of radiation disturbance experiment:
When the total length of the antenna is greater than 1/20 of the signal wavelength λ, effective radiation will be emitted to the space. When the length of the antenna is an integer multiple of λ/2, the radiated energy is the largest. When the noise frequency is greater than 30MHz, the cables, openings, and slits of electronic equipment are likely to meet the above conditions, resulting in radiation emission.
5. Electrostatic discharge ESD
Standard: IEC 61000-4-2 Criteria B
The purpose is to test the ability of a single device or system to resist electrostatic discharge interference.
Experimental principle: The ESD experiment is to simulate the electrostatic discharge of the human body or the object when it touches the equipment or the discharge of the human body or the object to the neighboring objects, including the direct exchange of energy, causing damage to the device or the near field caused by the discharge (electric field and magnetic field). Change), causing malfunction of the equipment.
6. Radiation immunity RS
Standard: IEC 61000-4-3 Criteria A
The purpose is to test the ability of a single device or system to resist electric field interference.
7. Fast pulse group EFT/Burst
Standard: IEC 61000-4-4 Criteria B
The purpose of the experiment is to investigate the ability of a single device or system to resist fast transient interference. These transient disturbances are caused by transient actions such as the interruption of inductive loads, resulting in the emergence of pulse groups. The pulse repetition frequency is high, the rise time is short, and the energy of a single pulse Low levels can cause equipment malfunctions.
8. Lightning surge surge
Standard: IEC 61000-4-5 Criteria B
The purpose of the experiment is to investigate the ability of the EUT to resist surge interference. These transient disturbances are caused by faults and short circuits of other equipment, main power system switching, and indirect lightning strikes.
9. Conducted radio frequency interference CS
Standard: IEC 61000-4-6 Criteria A
The purpose of the experiment is to investigate the ability of a single device or system to resist conducted disturbances.
Experimental principle: Mainly investigate the immunity of 0.15MHz-80MHz continuous interference voltage introduced from wires or cables.
10. Rated power frequency magnetic field
Standard: IEC 61000-4-8 Criteria A
The purpose of the experiment is to investigate the ability of EUT to resist magnetic field interference.
*For industrial environment requirements
*For magnetically sensitive devices, such as Hall elements
11. Voltage dips and dips
Standard: IEC 61000-4-11 Criteria B & C
The purpose of the experiment is to investigate the ability of the EUT to resist voltage drops and sags.